Protuberance Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
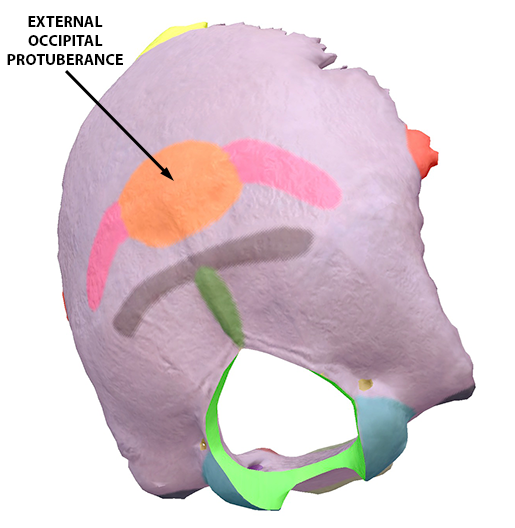
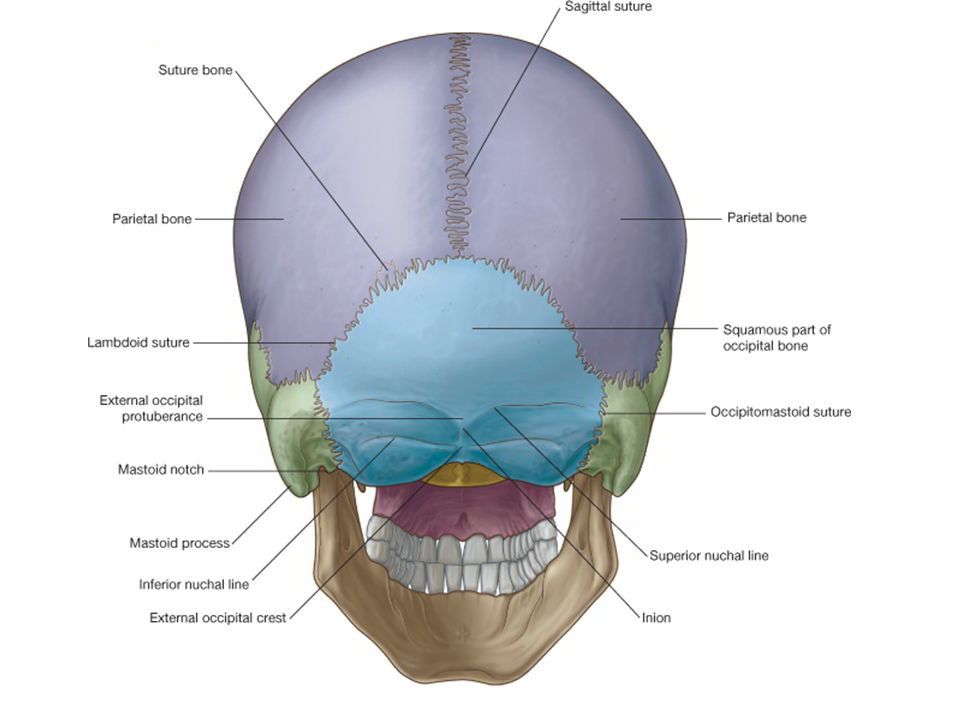
The occipital squama is the larger, more posterior portion of the external occipital bone. It is a thin, flat bone that forms the base of the skull and contributes to the formation of the posterior cranial fossa.The occipital squama is marked by several prominent features, including the external occipital protuberance, the external occipital crest, and the superior nuchal lines.

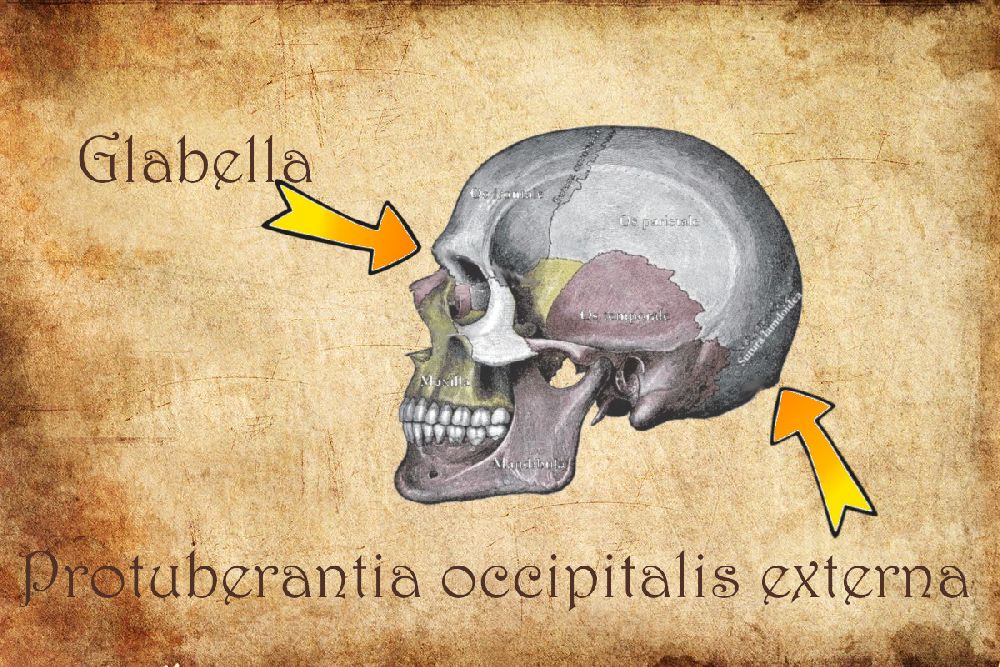
External Occipital Protuberance Palpation / External occipital protuberance a site for
Protuberantia occipitalis externa Clavicula Acromion Spina scapulae Angulus inferior Plica axillaris posterior Musculus erector spinae Os coxae Os sacrum Os coccygis Tuber ischiadicum Palpable bony structures 11071-01_CH01.qxd 3/28/08 10:05 AM Page 4. PLATE 1-03 PAGE 7 Chapter 1 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Atlas of Anatomy
Prominent External Occipital Protuberance Radiology
protuberantia occipitalis externa: TA98: A02.1.04.022: TA2: 568: FMA: 75752: Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] Near the middle of the squamous part of occipital bone is the external occipital protuberance, the highest point of which is referred to as the inion.
Skull Bone Markings Inferior View Part 2
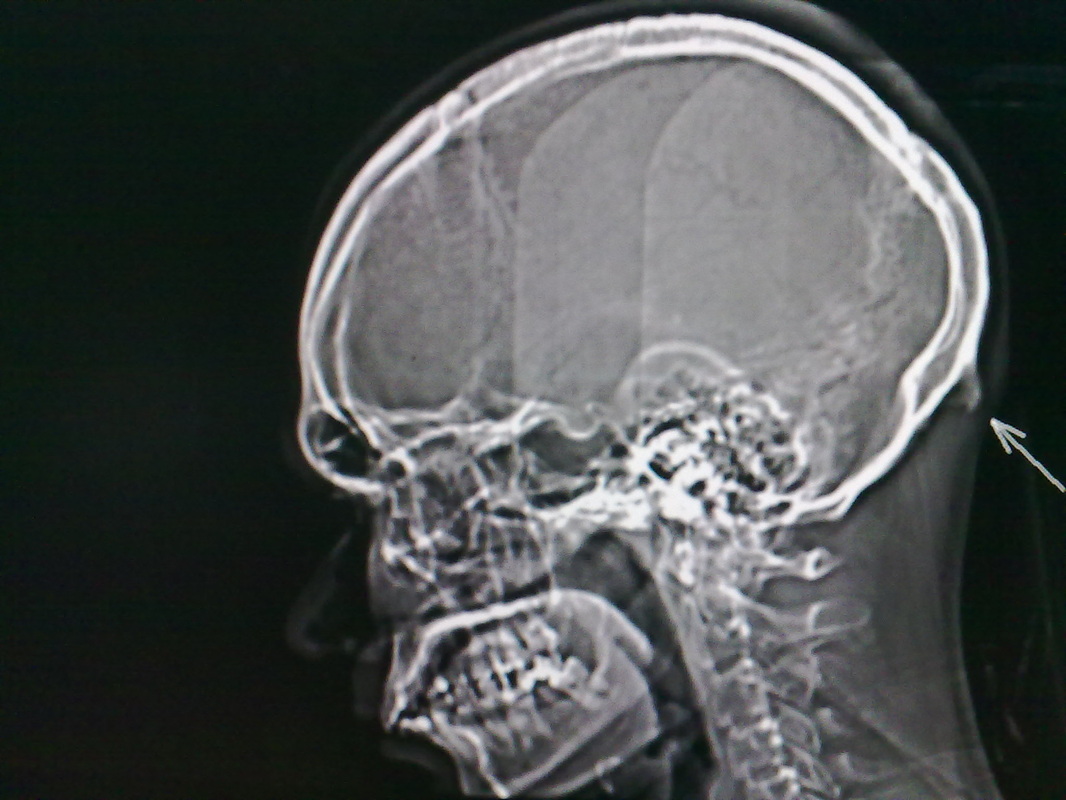
Epidemiology. It is common in males and hence is often used in forensic investigations for gender determination 1.. Clinical presentation. It is an anatomical variant which is usually noticed incidentally radiographically, although it can become symptomatic with affected patients describing a tender bony swelling at the back of the neck causing pain especially while lying down 1.

Protuberantia occipitalis externa MedkoM
Protuberantia occipitalis externa 1/5. Synonyms: Inion The squamous part is the largest of all four and contains both internal and external surfaces. A palpable prominence known as the external occipital protuberance lies on the midline of the external surface which serves as an attachment for the trapezius muscle.
Terminologia Anatomica(TA)に基づく解剖学
External Occipital Protuberance (EOP) enlargement has been recently reported to increase in young adults, with a putative link with postural factors such as the use of smartphones. This study aims.
Vom Skelett zum Geschlecht Miss Jones
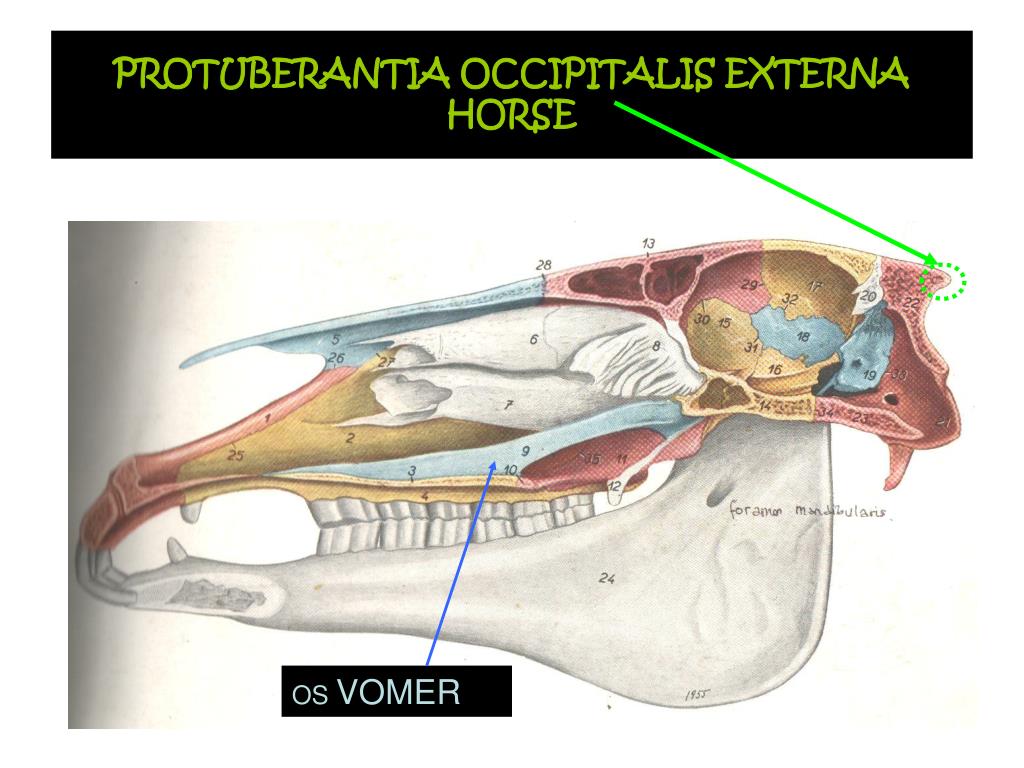
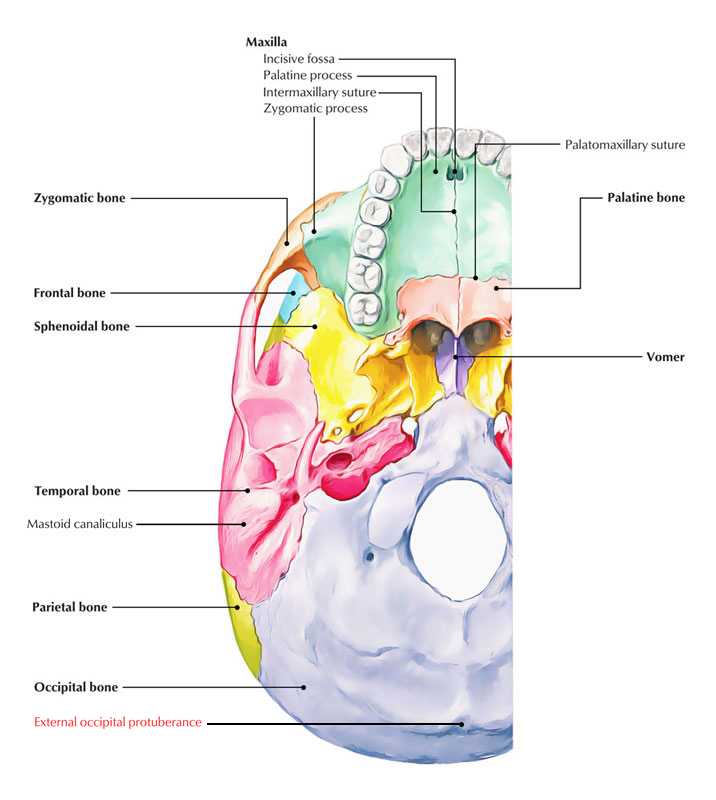
Near the line where it unites to the interparietal bone, the squamous part of the occipital bone shows the transversal prominence of the external occipital protuberance (protuberantia occipitalis externa). In species like Dogs or Horses, where the occipital reflexes on the dorsal surface of the head, this protuberance occupies the upmost point of the cranium and marks the dorsal elbow of the.
Protuberanta occipitala externa Despre viața din România
Protuberantia occipitalis externa Read more. Description. The external occipital protuberance is the palpable prominence found along the external aspect of the squamous part of occipital bone. It is located at the point along the midline where the occipital and nuchal planes meet. It consists of the inion, which is a craniometric point located.

El Baúl Radiológico PROTUBERANCIA OCCIPITAL EXTERNA (Ossified Spur on the External Occipital
protuberantia occipitalis interna: TA98: A02.1.04.029: TA2: 575: FMA: 75755: Anatomical terms of bone [edit on Wikidata] Along the internal surface of the occipital bone, at the point of intersection of the four divisions of the cruciform eminence, is the internal occipital protuberance.

External occipital protuberance a site for attachment of muscles and ligaments Body bones
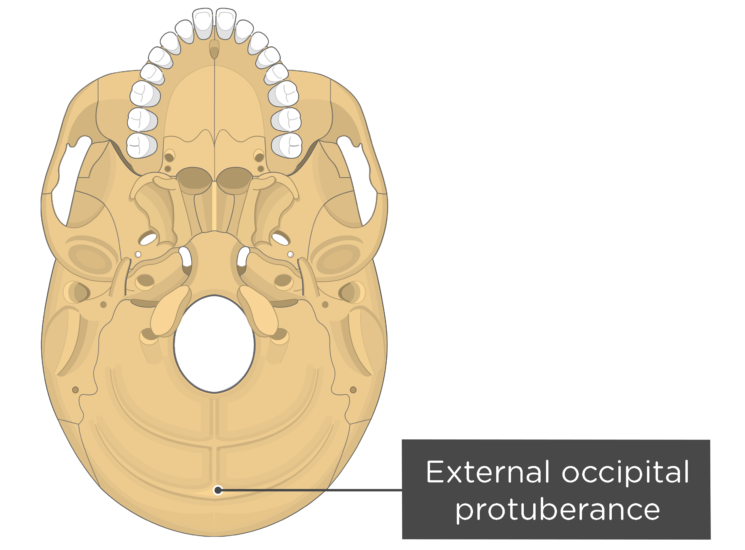
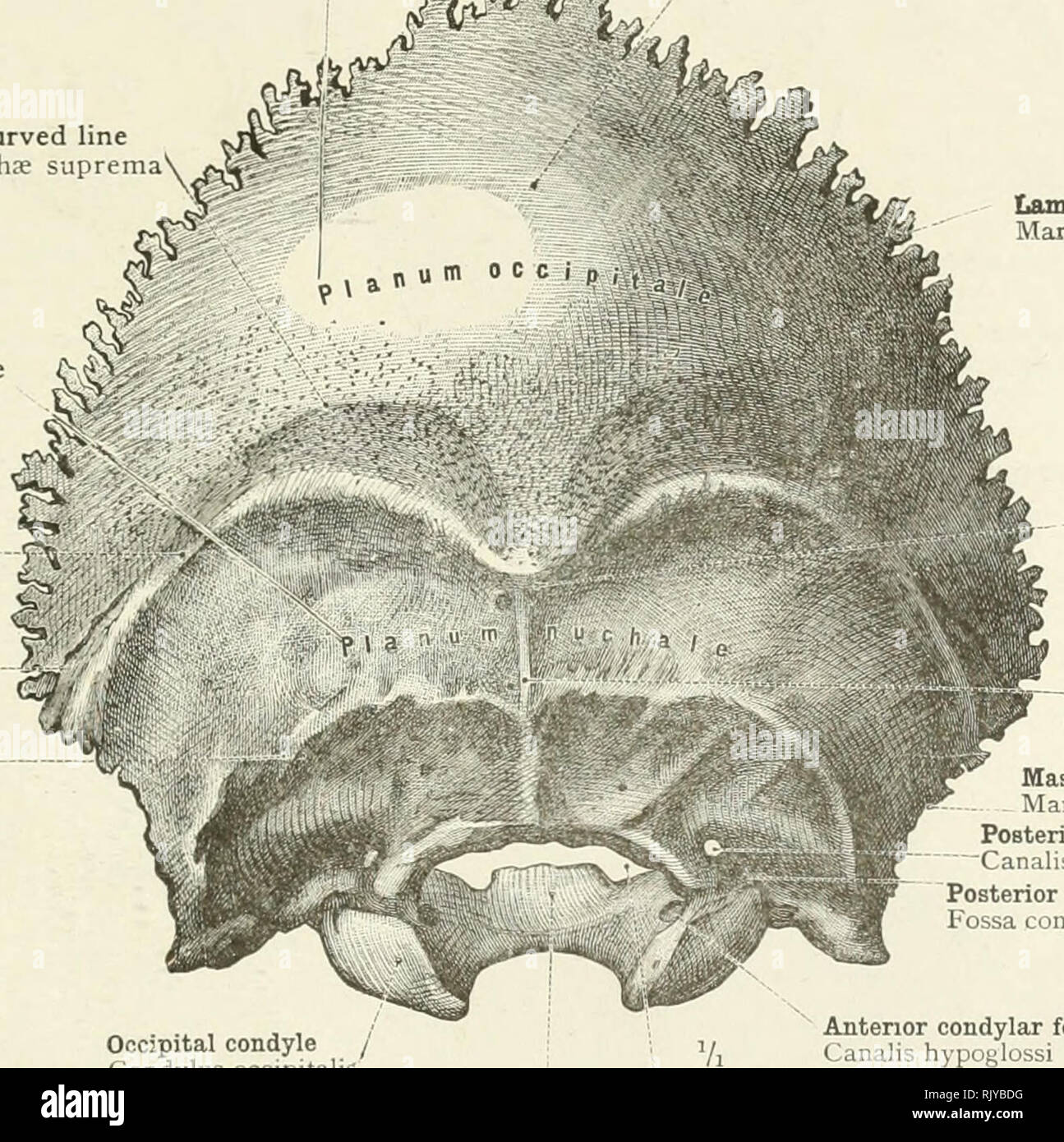
Dorsal aspect of occipital bone. The prominent feature of the squama's external surface is the protuberance, an easily palpable point known in the craniometry as inion. The list of terms: Planum occipitale - Occipital plane Protuberantia occipitalis externa - External occipital protuberance Linea nuchalis suprema - Highest nuchal line Linea nuchalis superior - Superior nuchal line
PPT OSTEOLOGY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3720738
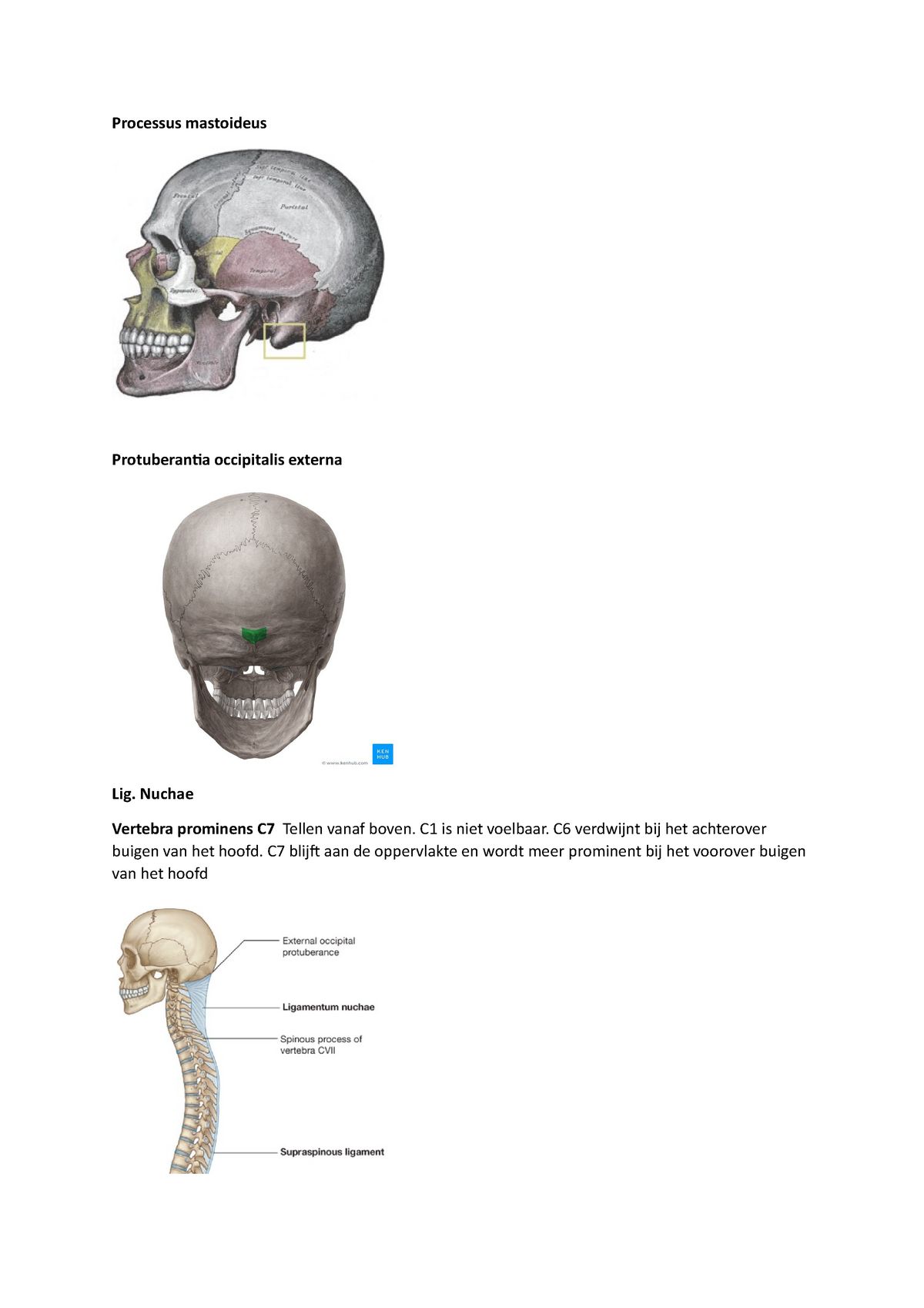
Case Discussion. External occipital protuberance is a midline bony prominence in the occipital bone that ligamentum nuchae and trapezius muscle attach to its tip. The tentorium cerebelli attaches to its internal surface. Exaggerated external occipital protuberance also is known as an occipital spur.
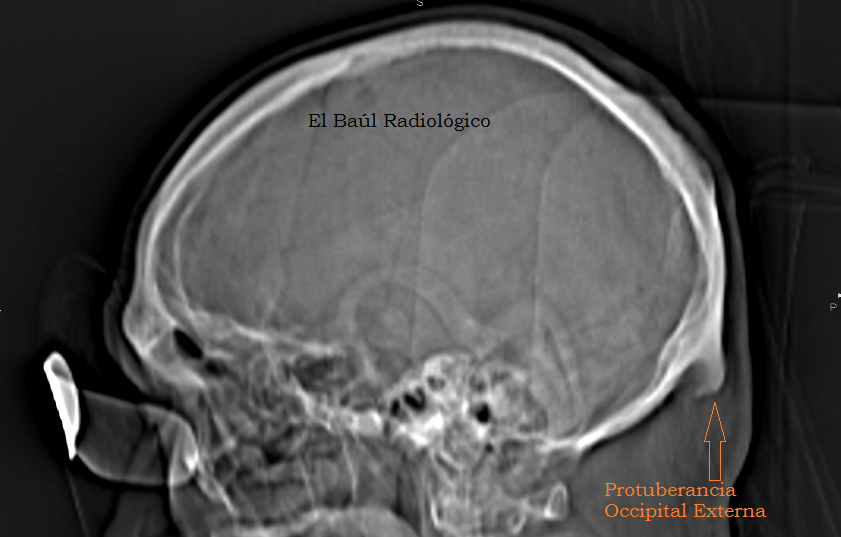
El Baúl Radiológico PROTUBERANCIA OCCIPITAL EXTERNA (Ossified Spur on the External Occipital
External occipital protuberance (EOP) is a midline bony prominence in the occipital bone that ligamentum nuchae and trapezius muscle attach to its tip that named Inion. The tentorium cerebelli attaches to its internal surface. Entheses are the sites of ligament, tendon or joint capsule attachment to the bone.
Occipital Bone Markings
Occipital protuberance. Occipital protuberance can refer to: Internal occipital protuberance. External occipital protuberance. This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Occipital protuberance. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article.

External occipital protuberance (Protuberantia occipitalis externa); Image Yousun Koh Skull
external occipital protuberance: [TA] a prominence about the center of the outer surface of the squamous portion of the occipital bone, giving attachment to the ligamentum nuchae. Synonym(s): protuberantia occipitalis externa [TA]
Anatomie lijst met figuren Processus mastoideus Protuberantia occipitalis externa Lig. Nuchae
Protuberantia occipitalis externa - External occipital protuberance Linea nuchalis superior - Superior nuchal line Linea nuchalis inferior - Inferior nuchal line Crista occipitalis externa - External occipital crest Foramen magnum. That illustration shows canals of the base of the skull, which usually is more challenging to localize.
External Occipital Protuberance Earth's Lab
Protuberantia occipitalis externa. Definition. The under surface of the jugular process is rough, and gives attachment to the Rectus capitis lateralis muscle and the lateral atlantoöccipital ligament; from this surface an eminence, the paramastoid process,sometimes projects downward, and may be of sufficient length to reach, and articulate.